Inflation Simulation in Capitalism Lab
When you start a new game with the inflation option enabled, inflation impacts nearly everything with a monetary value, including product prices, land costs, building expenses, salaries, firm operating costs, and more.
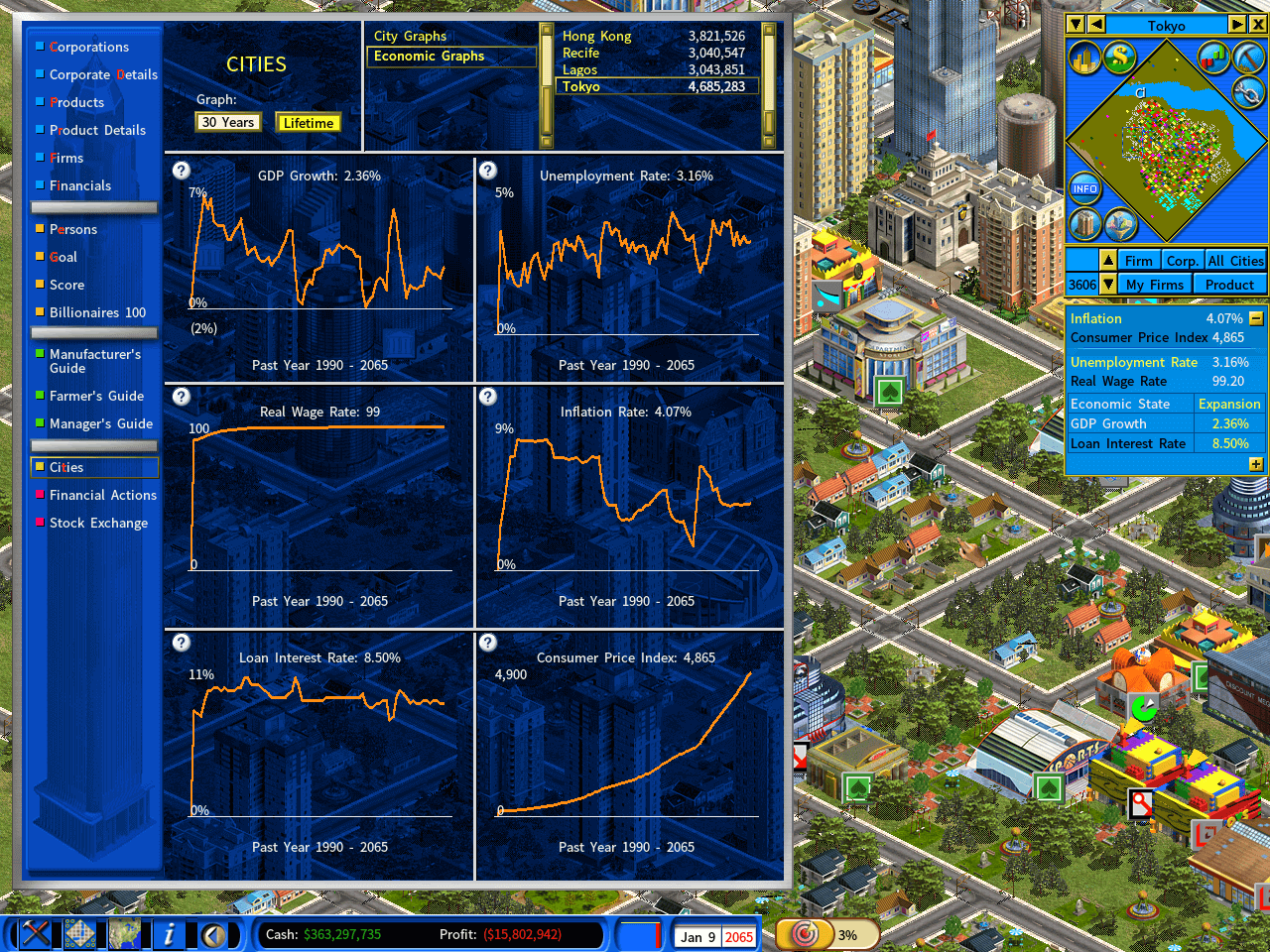
Automatically Adjusting Prices Based on Inflation
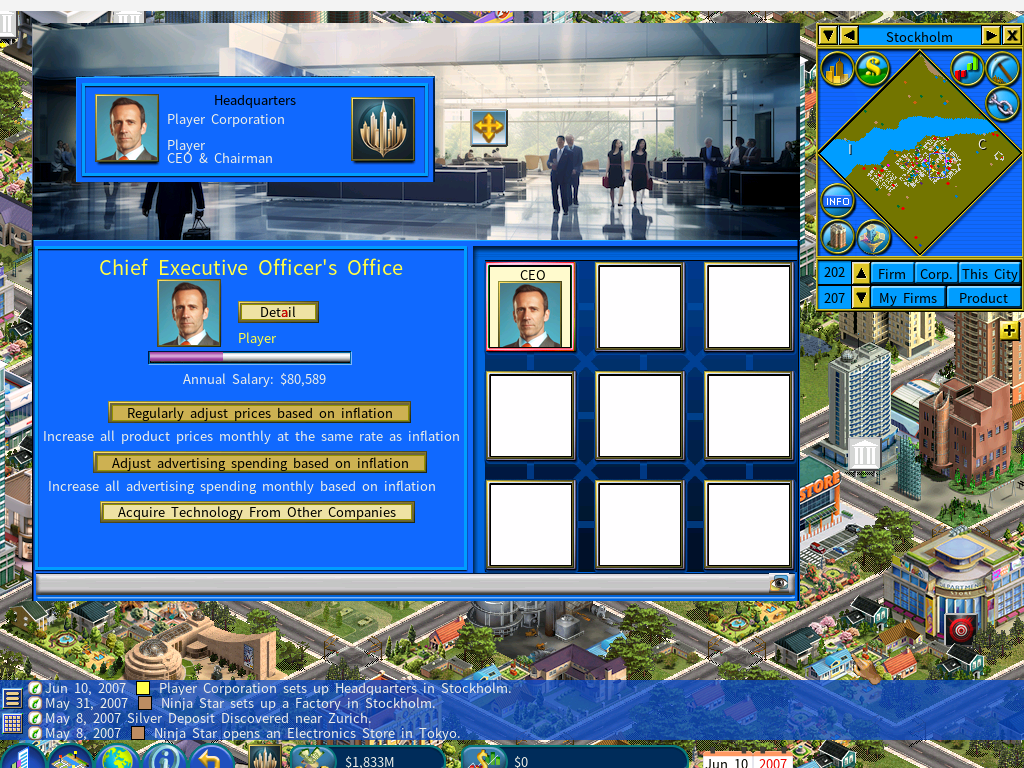
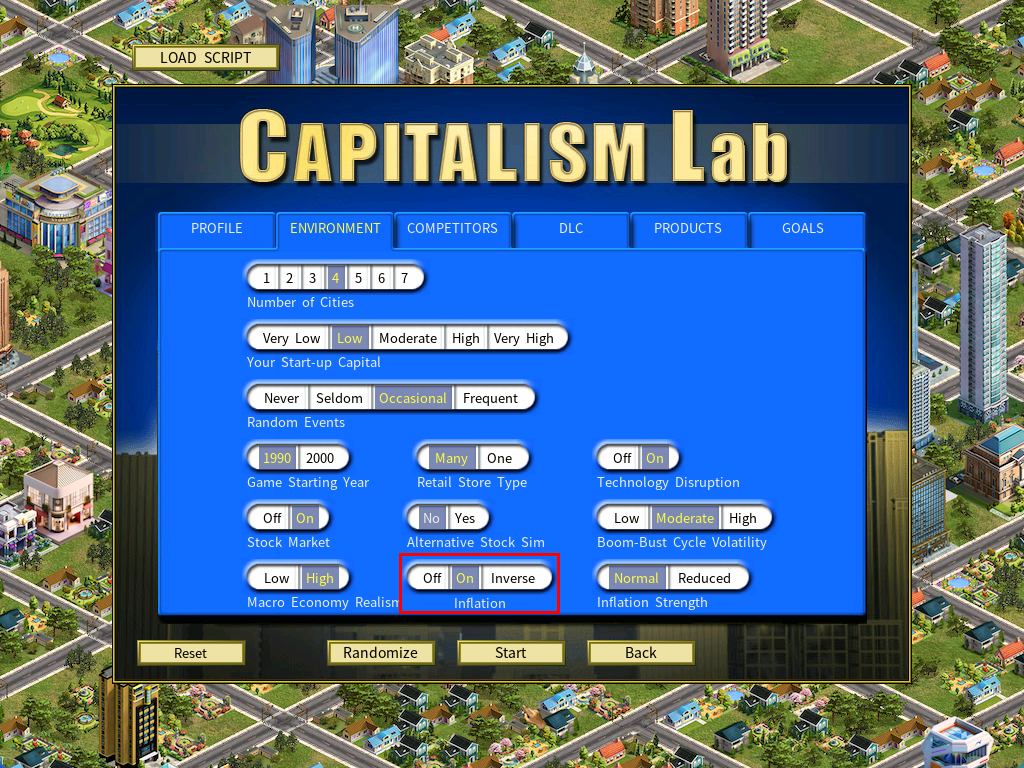
Special “Inverse Inflation” mode
There is a special mode called “Inverse Inflation,” where cash loses its purchasing power as a result of inflation. The Purchasing Power Index starts at 100% and diminishes during years of inflation. All cash and loan amounts shrink in accordance with this index.
If you simply hold cash and do not make investments, you will see your cash decrease in value along with its purchasing power. To prevent your wealth from shrinking, you must actively invest your cash into assets.
It is a fact that cash always loses purchasing power in the face of inflation, whether the inflation mode is set to “normal” or “inverse.” However, the psychological impact of inflation may feel greater when you see the direct shrinking of your cash value.
In contrast, deflation increases the purchasing power of your cash. During times of deflation, you may notice your cash amount increasing. As a result, it may be wise to liquidate and hold as much cash as possible during periods of deflation.
Loans behave in the opposite way to cash. During inflation, your outstanding loan amount decreases, whereas during deflation, it increases. Therefore, it is often a smarter strategy to take loans during periods of high inflation and repay them when deflation occurs.
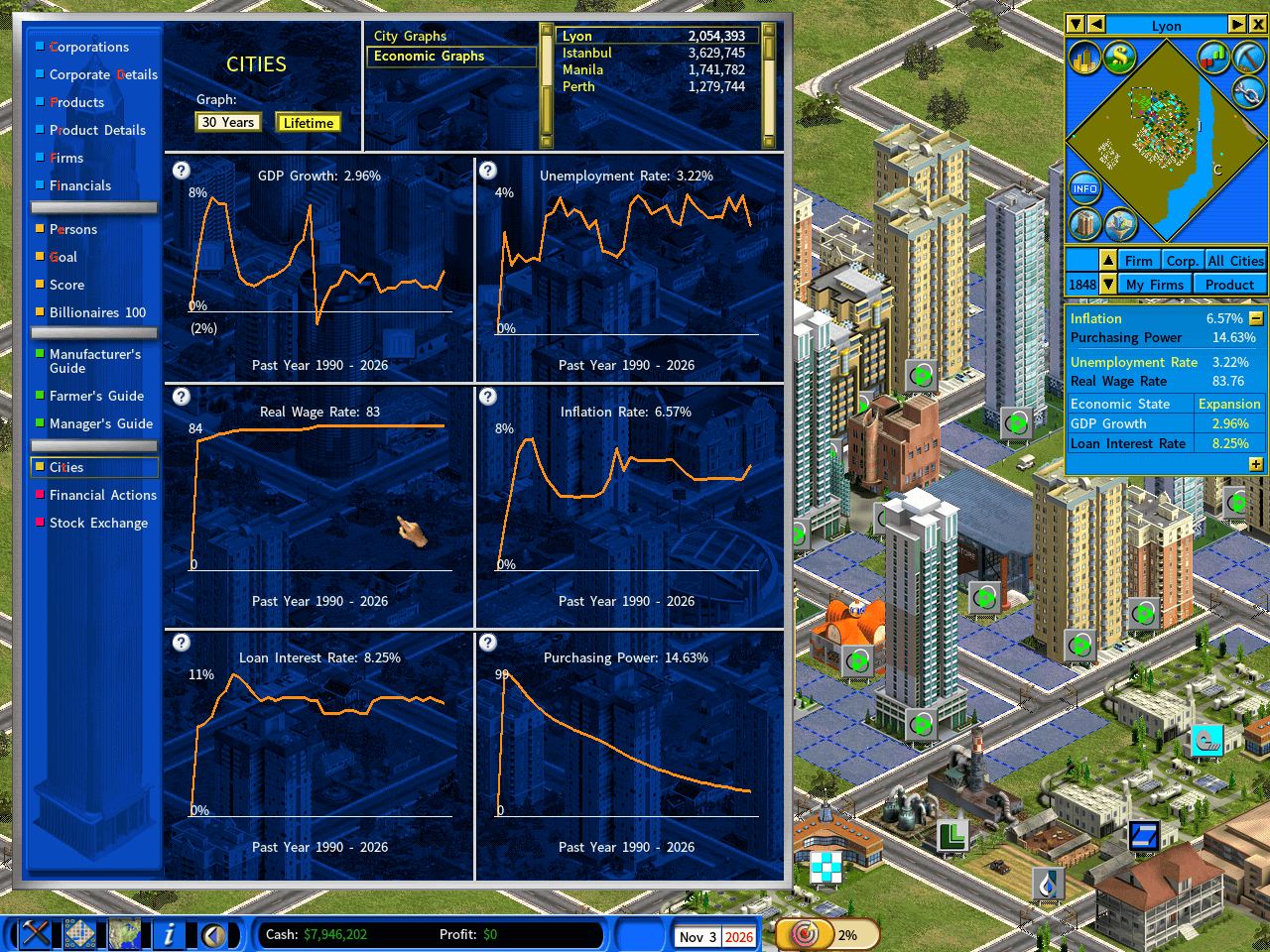
Under the “Inverse Inflation” mode, even if you take no action, your cash amount will decrease, whereas the values of your land and resource assets remain unaffected by inflation.
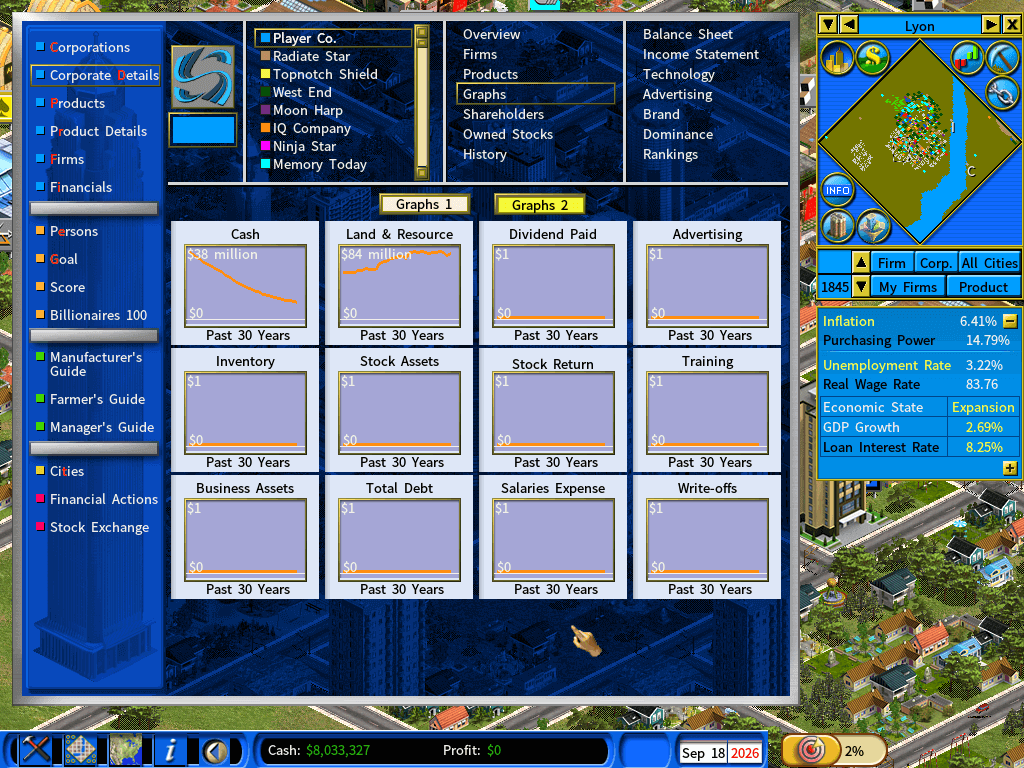
To enable the “Inverse Inflation” mode, select the Environment page from the New Game Settings menu and set the Inflation setting to Inverse.
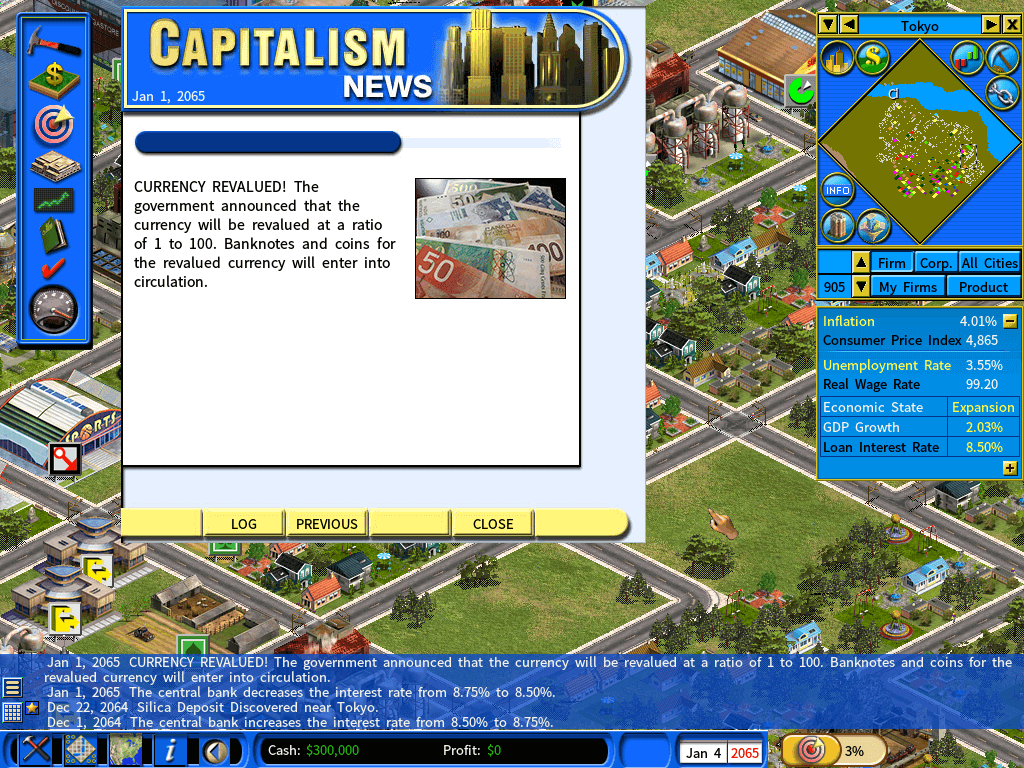
Revaluation of Currency in Times of Hyperinflation
Strategy Guide for Turning Inflation into Opportunity in Capitalism Lab
Capitalism Lab is a sophisticated business simulation game that immerses players in a dynamic economic environment. A key feature of its Enhanced Macroeconomic Simulation is the inflation mechanic, which mirrors real-world economic principles. This article expands on the Inflation Simulation feature, detailing the driving forces of inflation, its gameplay implications, including opportunities and risks, and how players can influence inflation through their actions.
Driving Forces of Inflation
Inflation in Capitalism Lab is driven by macroeconomic factors simulated within the game’s economic engine. The following are key drivers:
- Monetary Policy: The game’s central bank adjusts interest rates in response to inflation levels. Loose monetary policies, characterized by ample money supply and low interest rates, can fuel inflation by encouraging spending and investment. Conversely, high inflation prompts the central bank to raise interest rates to cool the economy, potentially leading to a recession (Enhanced Macroeconomic Simulation).
- Economic Indicators:
- GDP Growth: High GDP growth increases consumer and investor confidence, leading to greater spending and investment, which can drive inflation (Guide to Boosting GDP Growth)
- Low Unemployment: A low unemployment rate boosts consumer spending power, further fueling demand-driven inflation.
- Economic Cycles: The game simulates boom-bust cycles where inflation often rises during economic expansion. If inflation becomes excessive, the central bank intervenes by raising interest rates, which may trigger a recession to stabilize prices.
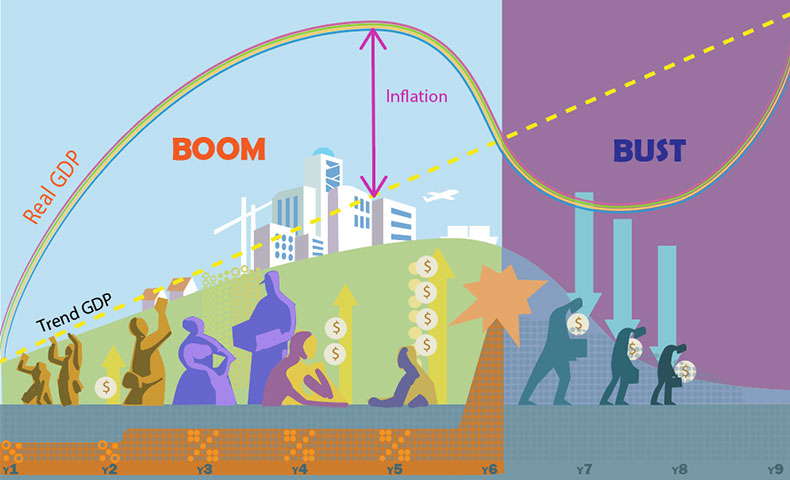
These factors are part of the game’s macroeconomic simulation, creating a dynamic environment where inflation fluctuates based on economic conditions.
Gameplay Implications
Inflation significantly impacts gameplay, affecting costs, prices, and strategic decisions. Below are the effects, opportunities, and risks associated with inflation.
Effects of Inflation
When the inflation option is enabled at the start of a new game, it affects nearly every monetary aspect:
- Price Increases: Product prices, land costs, building expenses, salaries, and firm operating costs rise with inflation.
- Inverse Inflation Mode: In this special mode, cash loses purchasing power as the Purchasing Power Index diminishes. Cash and loan amounts shrink accordingly, while land and resource assets remain unaffected.
- Hyperinflation: At extreme inflation levels (10,000%), banks issue new banknotes worth 1% of the current currency to make figures manageable, simulating real-world currency revaluation.
Opportunities
Inflation creates strategic opportunities for savvy players:
- Asset Investment: Investing in assets like real estate, which appreciate with inflation, preserves and grows wealth. Forum discussions highlight that rents increase with inflation, making real estate a lucrative investment (Investing in Real Estate).
- Strategic Borrowing: In Inverse Inflation Mode, taking loans during high inflation is advantageous as the real value of debt decreases over time. Players can repay loans during deflation when cash gains purchasing power.
- Price and Advertising Adjustments: Players can enable automatic adjustments for product prices and advertising budgets via the CEO’s office, ensuring competitiveness. Options include “Regularly adjust prices based on inflation” and “Adjust advertising spending based on inflation.”
Risks
Inflation also poses challenges that require careful management:
- Underpricing: Failing to adjust product prices can result in selling below market value, reducing profitability.
- Cash Devaluation: Holding excessive cash during inflation, especially in Inverse Inflation Mode, leads to a loss of purchasing power, as cash value diminishes.
- Deflationary Risks: During deflation, holding assets may be less beneficial, and players should prioritize cash holdings to capitalize on increased purchasing power.
- Economic Recession: If inflation spikes, the central bank may raise interest rates aggressively, potentially causing a recession that reduces consumer demand and impacts business performance.
Table: Opportunities and Risks of Inflation
| Aspect | Opportunities | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Management | Invest in real estate or other assets that appreciate with inflation. | Holding cash during inflation leads to loss of purchasing power. |
| Borrowing | Take loans during high inflation to benefit from reduced real debt value. | High interest rates during inflation control may increase borrowing costs. |
| Pricing | Adjust prices automatically to maintain profitability. | Underpricing due to failure to adjust reduces profits. |
| Economic Cycles | Capitalize on economic booms to expand business. | Recessions triggered by high interest rates reduce consumer demand. |
Player Influence on Inflation
Players can influence inflation through their actions through the City Economic Simulation DLC.
Indirect Influence via Business Decisions
Players manage corporations and make strategic decisions that impact the economy:
- Business Expansion: Large-scale investments, such as building new factories or retail outlets, increase economic activity. This boosts the Investment component of GDP, leading to job creation, lower unemployment, higher wages, and increased consumer spending, which can drive inflation.
Direct Influence via the Role of Mayor
The City Economic Simulation DLC allows players to assume the role of mayor, providing greater control over fiscal policy:
- Government Spending: Constructing civic buildings, such as police stations or community facilities, involves government expenditure, which stimulates the economy and may contribute to inflation.
- Taxation Policies: Players can adjust tax rates to balance economic growth and public services, influencing consumer spending and economic activity.
- Limitations: Monetary policy, including interest rates and money supply, remains under the control of the game’s central bank, which adjusts policies in response to inflation and other economic indicators.
Conclusion
Inflation in Capitalism Lab adds depth and realism to the gameplay, challenging players to adapt to a dynamic economic environment. By understanding the driving forces—monetary policy, GDP growth, and unemployment—players can navigate the opportunities and risks inflation presents. Through strategic business decisions and, with the City Economic Simulation DLC, fiscal policy management, players can influence inflation indirectly while optimizing their corporate empires. The game’s realistic simulation of inflation, coupled with player-driven strategies, makes it a powerful tool for learning economic principles and mastering business strategy.
